In today’s digital age, where nearly every aspect of our lives is online—from banking and shopping to personal communications—ensuring the security of our data is paramount. Cryptography, the science of encoding and decoding information, plays a crucial role in safeguarding our digital lives. This blog post will explore how encryption techniques work to protect your data and why they are essential for maintaining privacy and security in the digital world.
Understanding Cryptography and Encryption
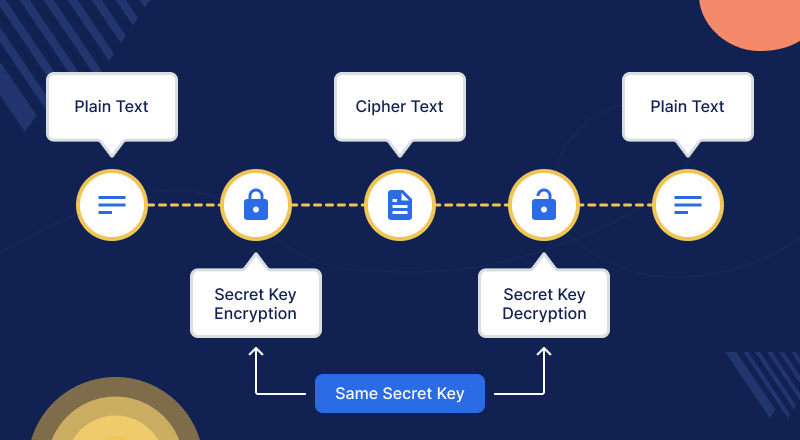
Cryptography is the practice of securing information by transforming it into an unreadable format, only to be deciphered by authorized parties. Encryption is the process of converting plaintext (readable data) into ciphertext (encoded data) using a cryptographic algorithm. The primary goal of encryption is to ensure that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be understood without the proper decryption key.
The Basics of Encryption
Encryption techniques are built on mathematical algorithms and keys. Here’s a basic overview:
- Algorithms: These are complex mathematical functions used to transform plaintext into ciphertext. Popular encryption algorithms include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), RSA, and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC).
- Keys: A key is a piece of information used by an encryption algorithm to convert plaintext into ciphertext. The key must be kept secret to ensure the security of the encryption.
- Encryption Process: During encryption, plaintext data is combined with an encryption algorithm and a key to produce ciphertext. This ciphertext is unintelligible to anyone who does not possess the key required for decryption.
- Decryption Process: To recover the original plaintext, the recipient uses a decryption key. The decryption algorithm reverses the encryption process, converting the ciphertext back into readable data.
Types of Encryption
There are several types of encryption, each suited to different needs and applications:
1. Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric Encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. This means that the key used to encrypt the data must also be used to decrypt it. Symmetric encryption is generally faster and more efficient but requires secure key management.
- Example: AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a widely used symmetric encryption algorithm that provides robust security and is commonly used to encrypt sensitive data such as files and communications.
2. Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric Encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, uses a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used for encryption, while the private key is used for decryption. This method enhances security by eliminating the need to share secret keys.
- Example: RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) is a well-known asymmetric encryption algorithm used for secure data transmission, digital signatures, and key exchange.
3. Hybrid Encryption
Hybrid Encryption combines symmetric and asymmetric encryption to leverage the strengths of both methods. Typically, asymmetric encryption is used to securely exchange a symmetric key, which is then used for the actual data encryption.
- Example: Many secure communication protocols, such as SSL/TLS used in HTTPS, use hybrid encryption to protect data transmitted over the internet.
How Encryption Protects Your Digital Life
Encryption techniques are vital for securing various aspects of digital life:
1. Securing Communications
When you send an email or message, encryption ensures that only the intended recipient can read it. For instance, end-to-end encryption used in messaging apps like Signal and WhatsApp ensures that even the service provider cannot access the content of your messages.
2. Protecting Data at Rest
Encryption protects data stored on your devices, such as smartphones and computers, by making it unreadable without the proper key. For example, full-disk encryption (FDE) encrypts all data on a disk drive, safeguarding it from unauthorized access if the device is lost or stolen.
3. Safeguarding Online Transactions
When you conduct online transactions, encryption secures your financial information. SSL/TLS protocols encrypt the data exchanged between your browser and a website, ensuring that sensitive information such as credit card details remains confidential during online purchases.
4. Ensuring Privacy in Cloud Storage
Cloud storage services use encryption to protect your files and data from unauthorized access. Data is encrypted before it is uploaded to the cloud and decrypted when you access it, ensuring that only you and authorized users can view your information.
Challenges and Considerations
While encryption is a powerful tool for protecting data, it is not without challenges:
- Key Management: Proper key management is crucial to maintaining security. Losing a key can result in the permanent loss of access to encrypted data, while improper handling can lead to unauthorized access.
- Performance Impact: Encryption can introduce latency and computational overhead, particularly in resource-constrained environments. Balancing security with performance is essential for optimal operation.
- Evolving Threats: As technology advances, so do cyber threats. Encryption methods must continually evolve to address new vulnerabilities and maintain security against sophisticated attacks.
The Future of Encryption
As digital threats become more sophisticated, encryption will continue to be a fundamental component of cybersecurity. Innovations such as quantum-resistant algorithms and advancements in cryptographic techniques will shape the future of data protection. Staying informed about these developments and adopting best practices for encryption will be essential for safeguarding digital information.
Conclusion
Cryptography and encryption are cornerstones of modern cybersecurity, protecting our digital lives from unauthorized access and ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of our data. By understanding how encryption techniques work and their importance in securing communications, transactions, and stored information, individuals and organizations can better appreciate the role of cryptography in maintaining digital privacy and security. As technology evolves, embracing advanced encryption methods will remain crucial for staying ahead of emerging threats and safeguarding our digital world.


Leave a Reply